Laser engravings are an excellent choice when it comes to making your business cards, scrapbook pages, or even personal goods stand out from the crowd. They’re also excellent if you want to give any of those “in-style” rings a more edgy appearance.
Because laser engraving is a useful and practical marking technique, its popularity grows daily. It is no wonder that it is becoming more and more popular. Laser technology advances, resulting in less costly laser equipment and more flexibility. Because of this, practically anybody may start a laser engraving service in their garage, which is a fantastic opportunity.
Laser engraving is a popular pastime that individuals of all ages and skills can enjoy, and it is particularly suitable for children. If you’re thinking about giving it a shot, this guide will provide you with all the information you need to get started.
We’ll go through the fundamentals of laser engraving, from the equipment you’ll need to the sorts of projects you may become involved with. Please continue reading for more information, whether you are a total newbie or simply searching for further information.
What Is Laser Engraving, and How Does It Work?
By cutting grooves into a hard, typically level surface, laser engraving allows you to inscribe a pattern onto it. Laser engraving is used to incise designs into hard, usually flat surfaces.
What Is a Laser Cutter, and How Does It Work?
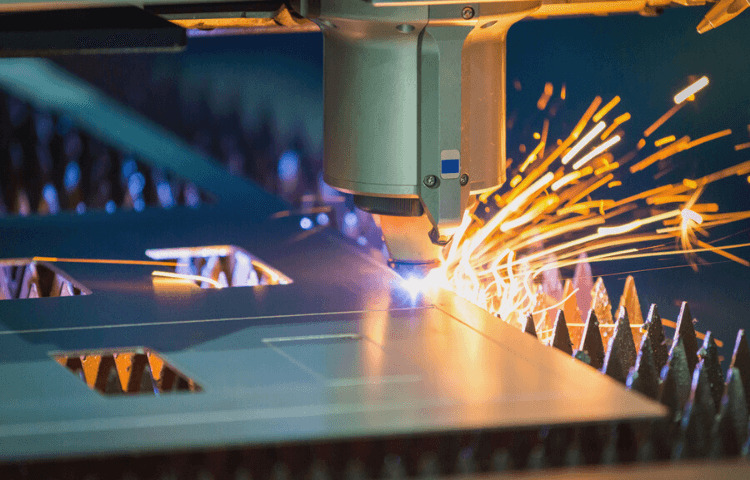
When cutting or engraving material, a laser cutter is a piece of computer-controlled equipment that employs a laser beam to accurately cut or engrave the material. A laser is essentially just a concentrated beam of light that has been greatly magnified.
The laser beam induces localized burning, melting, or vaporization of the substance. The sort of material that a laser can slice is classified by the characteristics of the laser and the power of the individual equipment.
The name “Laser” is an abbreviation for “Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation. The development of laser technology began in the 1960s.
Laser cutters are available in a variety of configurations. This article will concentrate on gas lasers in general and CO2 lasers in particular because these are the kinds of lasers that enthusiasts and small enterprises most widely utilized.
Other lasers include fiber and crystal lasers, primarily employed in industrial applications. Nonmetallic materials like paper, wood, acrylic, fabrics, and leather may be cut and engraved with CO2 laser cutters.
What is the Operation of a Laser Engraver?
Understanding how laser engraving technology works is essential for a laser engraving introduction. A laser beam is focused on a specific place on the surface of the substance being worked on.
It is possible to pre-determine the amount of material that will be melted and vaporized using the laser engraver’s parameters. A simple reflection of light by mirrors results in the accumulation of light energy in the form of heat.
The intensity of the engraving is controlled by varying the strength of the laser beam. After the procedure, the alteration in the surfaces of the material is visible, but it can also be perceived. The places where the engraving has been done may grow black.
People who desire a distinct hue can use multi-layered materials with varied colors on each layer. It is an excellent design strategy since it ensures uniformity in both appearance and design.
What are the Different Types of Laser Engraving Materials?

There are a plethora of different materials that can be etched. Paper, stone, glass, acrylic, wood, leather, and various other materials are most commonly used. The fact that not all substances must be engraved should not be overlooked.
For example, etching some polymers can be quite harmful in specific cases. Polycarbonate materials emit gasses that can quickly damage the laser engraver and can even be dangerous to human health if they are inhaled.
Additionally, due to their characteristics and potential health dangers, the following materials are not recommended for engraving: ABS, polystyrene foam, Lexan, polypropylene foam, fiberglass, epoxy, and coated carbon fiber.
What are Some Examples of Conventional Laser Engraving Applications?
Components of leather, metal, wood, plastic, and acrylic have benefited from this personalization method, which has grown increasingly popular. It is particularly useful for adding numbers, logos, photos, and serial numbers on parts, among other things.
Laser engraving is increasingly utilized to produce promotional goods like signs, pens, and displays.
Outside of the maker community, many people are interested in the potential of laser engraving to create things that are personalized with their names. Jewelry, including wedding bands that have been engraved, is one of the most noticeable uses.
What Kind of Software is Employed in Laser Engraving?

Because it is completely automatic, the laser engraver can operate independently. However, without software, it is almost worthless. Here is a list of some of the suggested software for use with laser engraving equipment.
Adobe Photoshop: This program is, without a doubt, one of the best available for engraving. It is the most feature-rich engraving program available today. Adobe Photoshop is a powerful application that both pros and amateurs can use to improve the overall quality of their work.
Adobe Illustrator: Illustrator, another product from Adobe, is THE graphics software. It has the greatest number of functions among vector graphic applications, which is likely the most extensive. Even though it is more difficult to grasp than other tools, Illustrator is well worth the time and effort invested in learning it.
AutoCAD: One of the most flexible software packages ever created, allows you to work more efficiently. Because of its extensive feature set and proclivity for storing drawings as vector files, this program is ideal for engraving applications.
What Exactly Can You Accomplish With a Laser Cutter?
In general, a laser cutter can do three types of tasks: engraving, cutting, and marking.
Engraving:

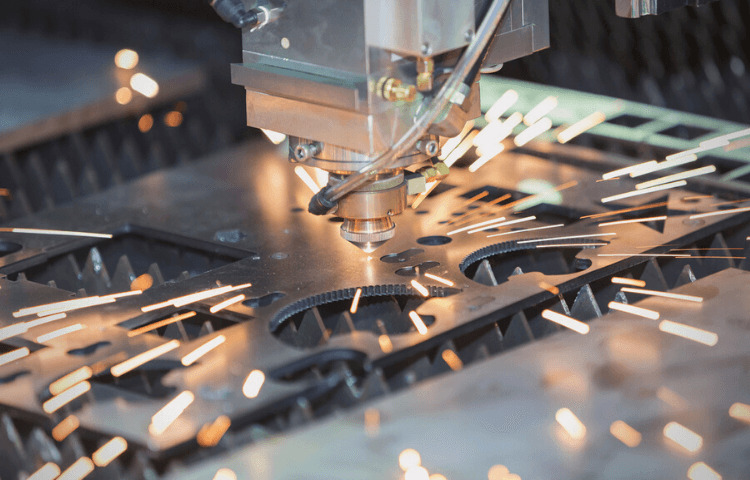
When the laser beam destroys portions of the top layer but does not cut completely through the material, this is referred to as laser engraving.
Cutting:

It is possible to generate a cut when a laser beam passes through the substance of the workpiece all the way through. A laser-cut is typically considered to be extremely accurate and clean. The appearance of the cut edges is determined by the material used.
Example: The margins of cut wood are often a deeper brown than the original wood, indicating that the wood has been chopped. After laser cutting, acrylic borders do not change color and have a lovely glossy finish, ideal for display purposes.
The kerf (cutting depth) of a laser cutter is extremely tiny. A kerf is a word used to describe the breadth of the groove created by a cutting tool. In addition to varying from one substance to another, this is also reliant on the exact parameters of the laser. Kerf will be anywhere from 0.05 mm and 0.5 mm.
Marking:

When the laser doesn’t quite remove material but rather alters the substance’s color, this is referred to as marking. When working with metals, CO2 laser cutters are mostly utilized for marking.
It is necessary to mark the workpiece surface with a marking solution (e.g., CerMark or Enduramark). The engraving process is carried out when the marking solution has dried. A permanent mark is made on metal by the laser’s heat bonding the solution to the surface of the metal.
What Type of Engraving Machine Should You Purchase?
The elements that impact the laser engraving machine that should be purchased will be discussed in further detail in this guide section.
First and foremost, while selecting laser engraving equipment, it is important to evaluate the intended use. What will be engraved on the surface of the machine? Small laser engravers are ideal for those who do not wish to engrave things in a commercial setting yet want a professional-looking result.
This sort of engraver is less expensive and is a significant benefit. The processing area is rather tiny, which is a drawback.
Another engraver is the crowdsourcing laser engraver used for crowdsourcing projects. Even though it is less expensive than other options, this engraver is typically low quality and represents a high-risk investment.
While industrial-grade engravers provide excellent results, they are expensive to purchase and may even be more costly to maintain!
Other considerations must be taken into account while selecting laser engraving equipment, in addition to size and application. These are some examples:
- The importance of safety.
- The process of cooling.
- Power supply.
- Exhaust air should be used.
Multifunctional machines are capable of performing a variety of tasks. These devices are extremely useful for various applications, including laser cutting, laser etching, laser engraving, 3D printing, and CNC carving. There is no need to purchase specialized machines for specialized jobs if a single machine can perform the functions of several other machines.
Designing for Laser Engraving: A Guideline
- To begin, familiarize yourself with the differences in the impacts that vector engraving and raster engraving have on different types of materials. Designing your component in this manner allows you to create visually beautiful and cost-effective designs. Learn about the underlying distinctions between these two approaches to problem-solving.
- Wood is not the same as stone in terms of hardness and durability. You should also be familiar with the various ways in which different materials respond to laser engraving.
- After that, construct the design in a graphics application such as Gimp or Photoshop for raster files or in a vector-based tool such as Illustrator, InkScape, and AutoCAD.
- The next steps are to import the document into the laser engraver and mount the component on the work platform. While tape may be appropriate for some designs and materials, some laser engravers provide mechanical options as an alternative.
- The manufacturer’s instructions should choose the laser engraving settings. Presets can be used to expedite this part of the process.
- Start the laser engraver and wait for it to finish.
- The majority of the time, post-processing laser engraving parts is not required. Install chains and glue sidewalls and components together if necessary to complete the assembly of the portion. In a nutshell, perform your magic.
What is the Best Way to Utilize a Laser Cutter?

Once you’ve completed your design, it’s time to go on to the next step: laser-cutting your materials. Laser cutters are extremely powerful pieces of equipment. The possibilities are endless with them, but they also risk being hazardous, so first and foremost, be cautious.
Before utilizing a laser cutter, ensure you have thoroughly read and comprehended all of the safety briefings that came with the machine. Furthermore, keep in mind that the spectrum of a CO2 laser is in the Infra-Red portion of the light spectrum, making it invisible to the human eye.
The red dot you see on the surface of a material with several machines is merely location assistance and not the laser beam cutting through the material.
Preparations:
First and foremost, ensure that your material will fit within the laser cutter’s work area and, if required, trim it to the appropriate size. Prepare to do some test cuts or engravings, and carry some spare material with you to ensure that everything goes well.
Working with a laser cutter does not necessitate the use of any additional equipment; however, in my opinion, the following tool has shown to be useful:
Measurement Tape: To measure and ensure that your finished items are correct in size
Masking Tape: It may be used to conceal the surface of your material to prevent burn marks and tape down lightweight fabrics.
Utility Knife: It is used for cutting material that has not been completely sliced through the laser cutter and for cutting paper products to size.
Settings:
The four most critical parameters on a laser cutter are power, speed, frequency, and the distance between the laser and the cutting surface.
Power: The output power of the laser is defined by this parameter. Typically, it is possible to select the percentage from 0 to 100%. A high level of power is required for cutting thick materials, whereas a lesser level of power is required for engraving and cutting thin paper products.
Speed: The pace at which this parameter controls the laser head moves. When engraving or cutting thin material, the speed is often set (or very close to) the highest possible speed.
Focus: As previously stated, the laser head contains a focusing lens for concentrating the laser beam. For most applications, the focus point (the point at which the laser beam is at its narrowest) should be on the material’s surface or just below it.
The substance must be kept at a specific distance from the lens to do this. The actual distance depends on the focusing lens used to capture the image.
Several laser machines have a motorized bed, adjusted in height and width to get the desired focus distance. It is also possible to manually modify the location of the material surface a.
Frequency: Specifically, the frequency parameter defines the number of laser pulses produced each second. The frequency of usage is dependent on the substance being utilized.
Time to Cut!
Lastly, you should be ready to make your initial cuts as soon as possible. It may take a few tries before finding the optimal parameters for your particular substrate.
In a test procedure, just one parameter should be changed at a time. For example, start with the power and experiment with other amounts in 5-10 percent increments to see what works best. Remember to jot down your settings after you are satisfied with your findings for future reference.
Materials for Laser Engraving: A Guide to the Possibilities
Laser engraving entails considerably more than simply securing any material in the work area and pressing a button to start the process.
It is important to remember that every material has its characteristics. These characteristics may sometimes assist you in accomplishing your design objective and sometimes make it difficult to reach your design goal. It is possible to learn about the qualities of the most common materials by looking at the following list.
1. Laser Engraving on Wood:

This laser engraving material comprises many sheets of wood that have been bonded together to form a single piece. A higher mechanical resistance, water resistance, and lightweight are achieved. These characteristics have made plywood a go-to material for architects, designers, artists, and craftspeople.
When it comes to laser engraving, plywood has the edge over real wood in several ways. When the latter is split into sheets, it shows grains in alternate colors resulting from different growth types occurring at different times of the year.
These distinctions are reflected in the laser-etched surfaces produced as a result. Generally speaking, the lighter regions will seem lighter, and the darker areas will appear darker when photographed.
To summarize, unless the desired appearance of your design is some sort of zebra pattern, you will be better off utilizing plywood with a uniform surface rather than patterned plywood.
In addition, while engraving hardwood, you should always use a greater laser power setting than normal. Then and only then can you achieve seamless outcomes.
2. Laser Engraving on Leather:
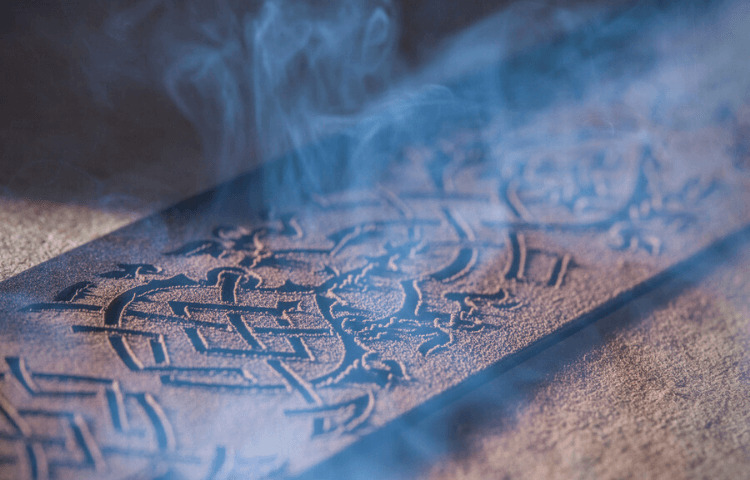

It is possible to laser engrave polished leather, resulting in an appearance comparable to hot-branding but without the heat. Avoid raster marking big leather areas since the leather may become powdery as a result. As a result, vector marking is highly suggested.
The fact that leather is a natural material means it may distort if too much force is given during laser engraving.
As a result of the numerous different types of leather available, it is impossible to formulate broad guidelines for laser engraving it. In this case, there is no way around choosing the appropriate laser engraving parameters for each kind of material individually.
3. Laser Engraving on Stone:

Experimentation has shown that laser engraving stone may be a simple piece of labor. The greatest results will be obtained by using polished stones. Make an effort to choose stones that have a smooth surface to minimize aberrations of the laser engraving theme.
Natural stones can be aligned with the laser by modeling clay to support the laser. When setting the laser’s focus, use an average number to get a uniform outcome throughout the board.
If your results are disappointing, you might want to experiment with a different Z-offset setting. This simple method may make a major difference in the outcome of your engraving.
Many laser engraver experts have reported that using a negative Z-offset value of 1mm or even more makes it simpler to process hard stones. The mechanics that underpin this solution are straightforward. The more energy that reaches the surface to be etched, the closer the surface is to the laser.
However, what should you do if your laser engraver does not have enough power to engrave on stone? Alternatively, when dealing with exceedingly hard stones that produce unsatisfactory results. Even in this case, it is possible to create patterns with strong contrasts!
Simply use masking tape to cover the glass surface. The design is then engraved onto the tape using a laser. After that, apply a small coat of paint to the area where the tape has been exposed using a paintbrush. After the paint has dried, carefully take away the masking tape and carefully remove the tape residue from the stone’s surface.
4. Laser Engraving on Glass:

It is possible to alter the laser’s impact on the glass surface by employing various practical approaches. A damp paper towel may produce a smoother surface finish and a brighter white engraving result.
Ensure there are no bubbles or overlaps in the image because this might affect the overall look. Once the engraving has been completed, the paper towel may be easily wiped away from the surface.
Application tape can be used as a substitute for paper towels. Applying tape is a great preventative strategy against surface roughening, like wet paper towels. The same warnings about air bubbles and overlaps apply here as well.
On the other hand, the final engraving color is not a dazzling white but rather a grayish-white. Removing the tape residue after the engraving process is completed is simple.
However, what should you do if your laser engraver does not have adequate power to engrave on glass? Even in this case, it is possible to create patterns with strong contrasts! Simply use masking tape to cover the glass surface.
The design is then engraved onto the tape using a laser. After that, apply a small coat of paint to the area where the tape has been exposed using a paintbrush. After the paint has dried, gently take away the tape and remove any tape residue that may have remained.
Benefits of Laser Engraving:
It is possible to customize and alter the appearance of your investment by engraving it! You may engrave anything you want on metal surfaces like silverware, including names, messages, and logos.
1. Versatility:
It is possible to use laser engravers to operate on various materials. As a result, DIY enthusiasts and small enterprises may reap major benefits from this adaptability.
You may engrave on various materials, like metals, glass, plastic, ceramic, and leather, to create a unique design. Adjusting the laser speed settings can also produce a variety of different outcomes. Slower engraving rates, for example, allow for more sustained laser beam exposure, which makes them more suitable for carving or deeper engravings.
2. Contact Lens Applications:

One of the most significant benefits of laser engraving is that it does not require physical touch. The laser beam does not make physical contact with the substance, but rather heat is used to achieve outcomes.
As a result, laser engraving is more efficient than traditional engraving procedures since there is no friction damage to the object’s surface. The laser beam vaporizes only the region that has been targeted; it does not affect the surrounding area.
3. Precision and Accuracy:
Suppose you have a piece of inventive laser-engraving equipment. In that case, you will never have to compromise with the quality of your engravings, whether you are creating individual engravings or elaborate patterns. Because the laser beam only operates on the surface area that has been targeted, you can expect 100 percent accuracy and precision.
4. Safety:

Laser engraving has taken the place of traditional technologies that depend on hazardous chemicals. By using protective laser safety eyewear, you can keep your eyes protected from the potentially hazardous effects and threats that lasers can cause.
The best aspect is that laser systems may be used in combination with computers, which allows them to be operated from a distance. Computers and eye protection are required to operate fiber laser equipment, which can be hazardous to the user if not used with the proper precautions.
5. Used by Multiple Industries:
Because of its adaptability and accuracy, the method has gained widespread acceptance worldwide. Laser engraving is used in various sectors to make personalized gifts, corporate souvenirs, bespoke jewelry, and other products.
Small firms rely on high-capacity equipment to identify automobile components, medical instruments, and nameplates, among other things.
Pros of Laser Engraving Machine:
- It is inexpensive.
- It has been pre-assembled so that you can get to work right away.
- However, when the focus is set later in the day, it takes an entire day to get the calibration back on track.
- There is no requirement for conversion or G code.
Cons of Laser Engraving Machine:
- There is an issue with the software, and you must restart it. The laser will stop if there is a power problem; in that instance, simply replace the external power source rather than the PC.
- To regulate the movements of the laser engraving machine, it uses a DVD-ROM stepper motor and a customized controller.
- This is a rather creative approach to lower the reward money. It comes with a software called laser carver, which is simple to operate and work with.
How to buy a Laser Engraving Machine?
Laser engravers are now available in a variety of forms and sizes. You may even begin with a tiny desktop computer to get your feet wet. Beyond the apparent size distinction, what else should you look for when selecting laser engraving equipment is described below. Here is a list of considerations that will assist you in making your decision.
Power Supply:
The laser unit consumes a significant amount of energy. On the other hand, some people are unaware of the other components’ power.
You’ll see the impact of the conditioning and air exhaustion modules on your power cost. So do the arithmetic and attempt to figure out if the benefits of installing a laser engraver in your workplace or shop outweigh the expenditures of setting up a company.
Laser Safety:
Keep an eye out for laser safety! When used irresponsibly, Class 4 lasers can cause significant harm. Before making a selection, take the time to consider your requirements carefully. You will sleep better at night if you choose a less powerful machine but still provides the job you require.
For each type of laser, improved eye protection is required. Make your investigation and find out if the laser engraver you have in mind comes with the protective glasses you require for it.
If this is not the case, any reputable manufacturer will inform you in advance of the laser class that has been integrated into the machines, allowing you to purchase the required protection glasses in advance.
Exhaust Air:
Laser engraving generates a great deal of debris. Many clouds of dust are created, dangerous if inhaled in large quantities.
This pipe must have a large diameter to remove all of the dust from the system. On the other hand, the engraver continues to be a health threat.
You should also be aware that air filters generate significant amounts of noise, which may be distracting if you plan to install a laser engraver in your office.
Cooling:
Even though powerful lasers require continual cooling, there are significant variations between the various cooling systems available. What is the operation of the laser’s cooling system? Tubes composed of metal or ceramic use air and have a lifespan of up to 5.5 years on average.
On the other hand, they are significantly more costly than cooling tubes constructed of glass. Water is used as a cooling agent in the latter case. The disadvantage of this approach is that it causes a significant deal of hassle since you must set a container next to the laser engraver to collect the wastewater.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Is laser engraving a simple process?
Using laser equipment to engrave is just as simple as printing on a regular printer at home. Starting with your favorite graphics application, you’ll need to design your file and establish the engraving plan before you can start engraving.
Is laser engraving a viable business venture?
With only a minimal initial investment, laser engraving may be a successful method to get your business off the ground in a booming market. Laser systems are so simple to operate that you’ll be able to begin using one in no time, and they’re so economical that they generally pay for themselves in a relatively short period as well.
Is it worthwhile to invest in laser engravers?
Because of the wide range of materials that laser engravers can etch, they are incredibly helpful. Before deciding which laser engraver to purchase, you should consider the various tasks you will be operating on and the materials you will be engraving.
Is laser cutting a profitable business venture?
Because individuals and small businesses now have access to the most up-to-date technology, starting a laser cutting business is a lucrative and flexible venture.
How long do laser engravers last before they need to be replaced?
The devices use a laser beam given in short pulses to provide the high-quality combustion and annealing required. Generally speaking, the equipment has a life expectancy of more than 35,000 hours and consumes little in consumables.
Bottom Line:
Laser engraving is a pleasant and creative activity that may be done in the comfort of one’s own home. This post has taught you how to get started with laser engraving for beginners, which has provided you with some excellent resources on the subject. Your newly acquired information must now be put into practice! Best of luck with your creation!




