When engraved, brass produces a beautiful gold finish, a high-end finish that is difficult to match. The metal, a mix of copper and zinc, may be oxidized to provide a deep black text appearance when oxidized.
With a modest quantity of lead and a significantly greater copper to zinc ratio than standard leaded brass, Premium Leaded Brass is simpler to engrave and oxidize to a truer black color. Using lasers in this technique is accomplished by engraving your drawings or messages on various surfaces such as glass, stone, plastic, and other materials.
You can even laser engrave brass if you want to go fancy. While this procedure differs from traditional engraving, which needs chisels and other tools to complete the task, it is nonetheless effective. This blog will demonstrate how to laser etch brass and the overall procedure involved in the process.
How Does Laser Engraving Brass Work?
Laser engraving materials with numbers, bar codes, and logos are a highly common branding usage on CO2 and fiber laser systems, and it is becoming increasingly popular.
Fiber lasers are an excellent choice for commercial marking applications because of their extended operating life, lack of necessary maintenance, and inexpensive cost relative to other laser technologies. These types of lasers generate a high-contrast, permanent impression that does not affect the item’s integrity under consideration.
When using a CO2 laser to mark bare metal, a specific spray is applied before the engraving process begins. The heat generated by the CO2 laser attaches the branding agent to the metal surfaces, resulting in a virtually indestructible mark.
CO2 lasers can mark various materials, including wood, acrylic, natural stone, and more, in a short amount of time and at a reasonable cost.
Both fiber laser systems and CO2 laser systems developed by Epilog may be operated from virtually any Windows-based program and are incredibly simple to operate.
How to Engrave and Mark Brass?
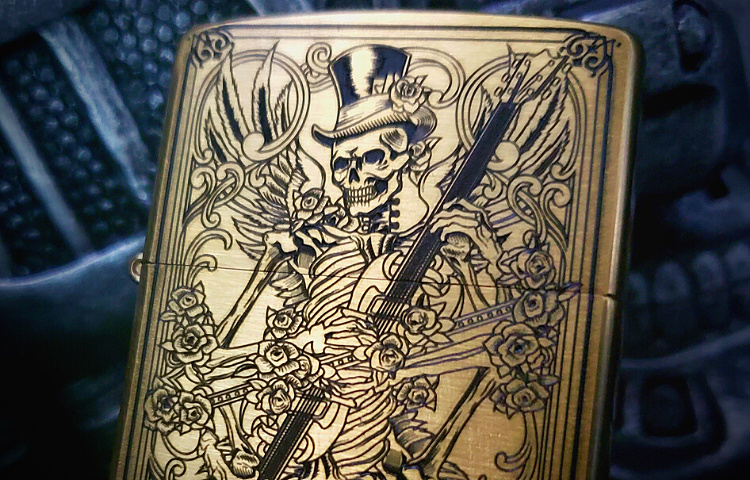

Because of the action of laser radiation, the procedure of laser engraving and marking takes place. Because it is focused on a narrow beam, it obtains a large proportion of energy, which causes heating and partial evaporation of the substance near the contact site and leads the material to decompose.
High process efficiency is accomplished by managing radiation, dosing energy, and frequency. This is especially important when working with certain metals, such as laser engraving brass for military applications.
The following are some of the advantages of using this material: It may be applied in various directions, such as in brass bolt marks or plate markings.
- Because it is simpler to mark and engrave than other materials, it is employed in various industrial applications.
- Several machinery components are made of this material, generally the first option. The electronics, automobile, industrial, mechanical, and precision engineering sectors are some businesses that use this material.
- It is often utilized in the home locks, handles, faucets, and other similar items.
- These materials are tubes, pipes, weather stripping, structural trim components such as radiators and fasteners, musical equipment, sanitary ware, decorative pieces, jewelry, and cartridge casting for weapons.
- It outlasts all other metals in service life and cost-effectiveness, unlike any other.
Laser Engraving Brass:
Brass is a metal alloy composed largely of copper and zinc that is durable and malleable. Brass is utilized in various sectors due to its low melting point and strong electrical and thermal conductivity, among other characteristics. When laser etching brass, a prominent dark imprint is left on the metal alloy, indicating that it has been etched.
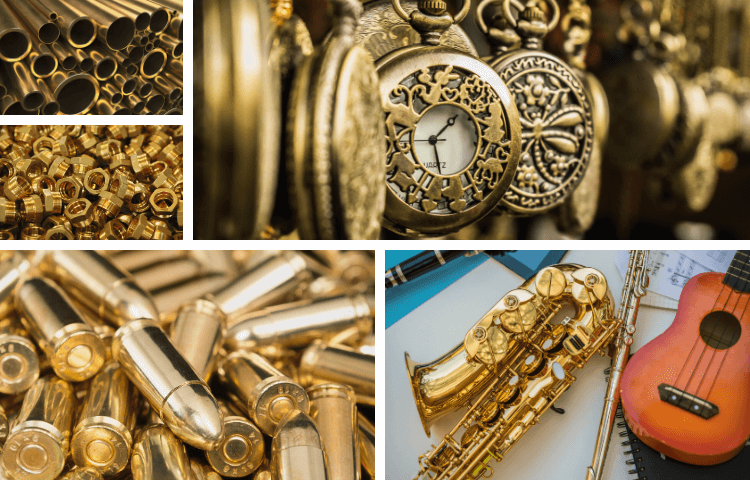

As a result, it is a widely used marking substance. Metals such as brass are typically found in the following:
- Plumbing fixtures
- Nuts and bolts
- Jewelry
- Pipe fittings
- Shell casings for ammunition
- Jazz instruments
- Precision instruments, such as gauges and clocks
What are the Benefits of Using a Brass Engraving and Marking System?
Here is a list of the advantages:
- Mechanical effect on the material is not present due to mechanical influence.
- The heat-affected material may be adjusted to a broad range of temperatures.
- The applied image’s maximum resistance to mechanical, chemical, and thermal effects.
- The rapidity with which brass vase marks are applied.
- The lack of supplies for rifle brass markings is an issue.
- Applications such as complex graphics, barcodes, photos, and end-to-end numbering are possible.
- The ability to switch between tasks for brass bell markings in a few seconds.
What is it That will Etch Brass?
[Switch and Lever] does an excellent job of describing the chemistry of the etching process and providing some advice on how to make the solution from granular ferric chloride. Ferric chloride works just as well on brass as it does on copper.
What is the Maximum Depth of Laser Engraving?
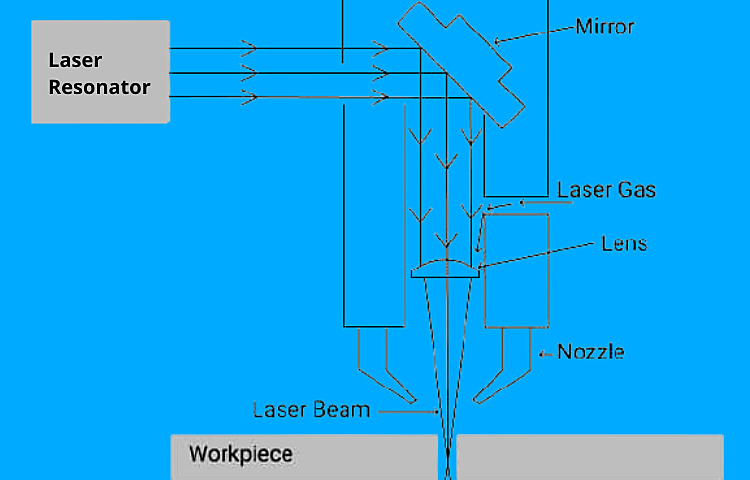
The depth of engraving may easily exceed a few millimeters in metals when it comes to deep engraving. On the other hand, standard laser engraving is often just a few microns deep, in sharp contrast.
On the other hand, traditional laser engraving may go down to 500 microns in depth. This is frequently the case when it comes to shot-blast resistant laser cutting.
The primary distinction between deep engraving and laser engraving is that deep engraving has additional standards for depth and aesthetics than laser engraving. On the other hand, laser engraving needs a high contrast to fulfill traceability standards, just as it does with laser etching.
Wrapping it Up:
Even though it is a relatively new art form, laser engraving is rapidly gaining popularity. In addition to engraving metals, plastics, glass, brass, and even wood, laser engravers can engrave various other materials.
Because of the exquisite detail that can be etched into a material by the laser beam, laser engraving is popular among those who want to do their custom work. The information contained in this blog post is provided in the hope that it has been of assistance to you.




