FDM 3D Printing is a type of 3D printing technology that uses an extruder to print thin layers of molten plastic. The term “FDM” stands for “fused deposition modeling” and refers to building up plastic on a build platform using a print head. The print head deposits material as it moves across the platform while depositing thin layers to be removed later without causing damage to the object being created.
This technology was originally used for rapid prototyping but has been adapted to create three-dimensional objects. The software and hardware involved in FDM 3D printing are similar to those used in SLA 3D Printing, though the process can be more time consuming and requires more skill.
3D printing technology has been used since the mid-2000s. Still, it has recently seen a surge in popularity thanks to its ability to produce high-quality parts that can be used in various industries.
What is FDM 3D Printer?
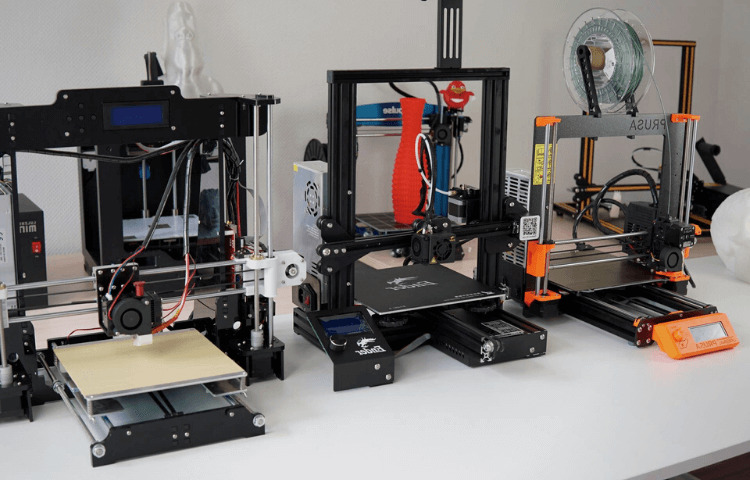
Fused deposition modeling (FDM) is an additive manufacturing process that combines extrusion and deposition to create 3D objects. The idea behind FDM is that you can make an object layer by layer and build up the object over time, much like a piece of wood would be made from wood chips.
This method was first developed in the 1980s by Wildon Farwell, who started experimenting with using polyurethane plastic for 3D printing. It wasn’t until much later that he discovered how to fuse multiple layers—but it was still an early version of what we know today as FDM!
Today, FDM is one of the most common methods for creating 3D-printed objects. It’s used for everything from making toys and model cars to building prosthetic limbs and medical devices such as hearing aids.
The earliest models were very large machines that used large amounts of electricity and metal powders to create objects in large quantities.
Today’s FDM 3D printers are much smaller and use less electricity than their predecessors. They can be used to print functional prototypes or small parts for manufacturing processes such as injection molding and extrusion blow molding.
FDM is one of the most common methods for creating 3D-printed objects. It’s used for everything from making toys and model cars to building prosthetic limbs and medical devices such as hearing aids.
FDM is one of the most commonly used methods in the industry because it allows companies to create complex objects efficiently and quickly. This means that FDM 3D printers can be used for both small-scale prototyping and large-scale production runs; they are also highly efficient for space-constrained environments such as hospitals, labs, airports, and schools.
How Does FDM 3D Printing Work?

3D printing is one of the most exciting fields in technology. While it may be intimidating to think about, there are plenty of resources out there that can help you get started.
Here’s a quick overview of how FDM 3D printing works:
FDM 3D printing uses a digital design uploaded to the 3D printer. Polymers such as ABS, PETG, PEI, and PEEK are melted and extruded through a nozzle. A series of heated beds form a platform on which the plastic cools and hardens into a solid object. Design is sent through a machine that converts it into plastic threads called Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM). This process involves taking the shape of plastic threads fed from a coil and through a nozzle.
The base with the base and the nozzle, both of which are controlled by a computer. The computer translates the object and its dimension into coordinates, making it possible for the nozzle and base to follow.
As each layer is printed, they’re cooled using water or another liquid cooling method. At this point, the printhead goes up so that more material can be added on top of what has already been printed. FDM does not use a photopolymer material like most other types of 3D printing do. Instead, it uses thermoplastic materials such as ABS and PETG that can be melted by the heat from an extruder and then extruded through a nozzle onto a bed that has been heated up to 220°C (428°F). The melted material cools and solidifies into a hard bond with the previous layer.
FDM printers can be controlled by either computer or by hand-held controls. These printers have nozzles that move across beds which contain the base and nozzle. The computer translates an object into coordinates so that it can be made possible for these nozzles to follow along with them.
Where Can FDM Use For?
FDM 3D printing is an additive manufacturing process used by businesses looking for a viable option that can deliver results. FDM 3D printers are competitively priced, and the best FDM 3D printers can be used for thermoplastics for food packaging and drug packaging, among many other common uses for this technology.
This development is perfect for anything ranging from Children’s toys to sports equipment. FDM-based 3D printers are also used for prototyping and their manufacturing process.
FDM printing is ideal for creating small parts and prototypes because it can handle high temperatures and mechanical stress. It is also used for creating end-use parts like jewelry, toys, and medical devices.
FDM 3D printing is also used to create extremely complex objects, especially small ones with lots of details.
The most common type of material used in FDM 3D printing is thermoplastic. The strong properties of thermoplastics make them ideal for creating prototypes because they can endure heat, chemicals, and mechanical stress. FDM 3D printing is a great way to make prototypes, but it can also be used to create end-use parts.
Another advantage of FDM 3D printers is that they can print in many colors and patterns. This allows designers to create highly customizable products that fit their brand perfectly.
Advantages of FDM 3D Printing:
- Easy To Handle:
FDM 3D printing is a great way to customize and create parts for your product. It can be used in manufacturing to print prototypes of new products or even create finished products. FDM, or Fused Deposition Modeling, is a 3D printing technology that allows you to create 3D objects from your computer. FDM printing technology is the most widely used 3D printing process today.
The benefit of FDM printing over other materials is that it is a very easy and versatile process, making it easy for designers, engineers, and hobbyists alike to use. The low cost of materials also makes it an attractive option when compared to other forms of 3D printing.
However, there are some drawbacks associated with FDM printing as well. It is difficult to control the quality of prints produced by this process as it relies on a number of variables, including temperature, speed, and pressure settings applied during each print session. However, with technological advances coming soon, we hope these issues will be resolved soon enough!
- FDM 3D Printing Is Cost-Efficient:
FDM 3D printing is a low-cost, efficient alternative to other 3D printing techniques.
The cost of building a prototype using FDM is much lower than other 3D printing techniques, including SLS and SLA. For example, if you need to build a prototype for $10,000, you will have to pay $5,000 to use SLS technology. However, if you want to build the same prototype with FDM 3D printing technology, you only need to pay $3,500.
This is because FDM 3D printing uses cheaper materials than SLS and SLA. This means more money is left over for other parts of your prototype development process.
- Flexible Options for Materials:
The flexibility of materials in FFF 3D printing FDM allows you to choose from a broad range of options and materials. You can print with various colors, offering versatility and flexibility.FDM is a popular choice for those looking to create prototypes and small-scale production runs, as it offers the flexibility of printing in a wide range of materials, building intricate models that last, and producing parts with color.
Millions of people use FDM daily to create everything from toys and gadgets to furniture, cars, and even houses!
- Availability of a Wide Range of Printers and Materials:
3D printing has become a popular and versatile solution for manufacturing, prototyping, and rapid product testing. The ability to create parts in metal, plastic, wood, and other materials has opened up new applications that were not possible with traditional manufacturing methods.
Many manufacturers offer various 3D printers with different capabilities and price points. Some printers are more affordable than others; however, they can still be quite expensive if you want to get the most out of your investment.
To determine which printer best fits your needs, consider how fast you need your parts to be printed (in minutes), what materials are available on the market today (e.g., metal), how much you’re willing to spend per part (in dollars), and what kind of reliability level is acceptable for your business (i.e., if it stops working or glitches out often).
- Least Time-Saving Technology:
FDM 3D printing is a time saver for businesses of all sizes, especially those with limited resources. Because it’s so accessible, it can be used by people who don’t have the necessary skills to create products with other types of 3D printers.
This is especially true for new businesses that haven’t yet invested in the equipment to use more advanced methods like SLA or SLS.
It’s also helpful for established businesses that want to scale up their production without investing in expensive machinery. FDM 3D printing is easy to understand, which makes it ideal for people who aren’t necessarily skilled in manufacturing processes.
In addition to being accessible, FDM 3D printing offers a simple solution that allows companies to create ready-to-use products once they are printed. This means less waste and time in creating prototypes before moving on to more complex fabrication techniques like SLA or SLS.”
Disadvantages of FDM 3D Printing:
- Little Details:
The main disadvantage of FDM 3D printing is that the nozzle size limits the details of finished prints. FDM 3D printing may not be suitable for high-quality models or intricate designs, while other technologies offer greater detail.
- Lack of Durability and Standard:
The biggest disadvantage of FDM 3D printing is its lack of durability and standard. The parts are usually made from a material that is easy to break down and make thinner, which means that the parts will be less sturdy than those made with other methods. The other big issue is that FDM 3D printers can only print standard-sized objects now.
- Design Inaccuracies: The design inaccuracies of FDM 3D printing are because it’s built on a layer-by-layer process, which means that it can’t create anything with intricate features or fine details due to how much time it takes to print each layer. Therefore, if you want something with intricate features or fine details, you’ll have to use another method like 3D modeling or laser cutting instead.
- Not Suitable for Large-Sized Parts:
Because FDM 3D printers don’t work well with large-sized objects (such as cars or furniture), they’re not very suitable for making these kinds of parts.
Applications of FDM 3D Printing:
- Low-Volume Production of Complex Parts:
FDM 3D printing is an ideal technology for producing complex parts. The process allows for rapid prototyping, allowing engineers to make models that can be tested more quickly and cost-effectively than traditional manufacturing techniques.
- Rapid Manufacturing:
FDM 3D printing lowers the cost of production by making it possible to produce larger parts at a lower price per item. This process allows for rapid prototyping and functional testing of new designs before they are mass-produced.
- Functional Testing:
FDM 3D printing allows for the functional testing of new designs before mass production, which reduces costs and improves quality control. This makes FDM 3D printing an ideal technology for creating functional test models or prototypes used in product development processes such as testing or validation.
- Engineering & Concept Models:
Engineers and concept modelers also use FDM 3D printing to create prototypes as a part of product development processes such as engineering design verification (EDV), system engineering, simulation, validation, analysis and evaluation (AVE), product design reviews (PDR), concept car design reviews (CCDR), etc.
Materials Used in FDM 3D Printing:
FDM 3D printing is a common method of 3D printing that has been around for decades, but the technology has only recently evolved to offer new capabilities. Most FDM 3D printers use plastic as their primary material, with some also offering support materials like wood and metal.
The most common FDM 3D printing materials are ABS, PLA, and their various blends. PLA is a type of plastic created from renewable resources that is non-toxic and biodegradable. It is used in many different industries, including manufacturing, construction, and even medical applications such as making surgical tools or medical implants.
Advanced FDM printers can also print with other specialized materials that offer higher heat resistance, impact resistance, chemical resistance, and rigidity.
Frequently Asked Question:
Can the FDM 3d printer deposit one-way direction?
FDM 3D printing can deposit one-way direction. This is a very important feature because it allows you to print with many materials and create various shapes.
Can I FDM 3d print a record?
At some level, wrong can say they 3D FDM technology can and has been used to print records!
How is 3d printing different than FDM?
In FDM 3D printing, your printer lays down thin layers of plastic, which cools and hardens in place. These layers are then separated by a laser so that the printed object will be impossible to damage.
In 3D printing, however, you create solid objects from melted plastic. These are then cured in their final form by an electron beam or heat lamp.
How to 3d print a miniature on an FDM printer?
Miniature 3D printing is making small models or sculptures using a 3D printer. However, FDM 3D printers aren’t ideal for printing miniatures. But many of the FDM printers on the market can print at very high resolutions.
How to add support for FDM 3d printing?
If someone is creating features with up to a 45° angle, it doesn’t require any support but features less than a 45° angle will need support. The more common type of support is called lettice support. It works well for nearly every type of 3D structure and is easy to create and customize.
What does PLA stand for in 3d printing?
PLA stands for Polylactic Acid, one of the popular materials used in 3D printing.
What is FDM technology in 3d printing?
The technology works with horizontal and vertical angles; an extrusion nozzle moves over a build platform in this procedure.
What is fused deposition modeling?
It is the technology in which the melt extrusion method is used to deposit filaments of thermal plastics. It is the process of building a physical object with successive layers of materials.
What is PLA 3d printing?
Polylactic Acid is the most popular material used in desktop 3D printing. It is the most popular printing material which is easy to use. It can be created at low temperature and doesn’t requires a heated bed.
What is PLA filament?
PLA stands for Polylactic Acid, the most popular material used in 3d printing.
When was FDM 3d printing invented?
FDM was invented in 1989 by Stratasys, Inc, with his wife, Lisa.
Bottom Line:
3D FDM printing is a revolutionary technology that has revolutionized how we create and manufacture products. It is a cost-effective and versatile process that can create objects of any size or shape. However, it also has some drawbacks, such as difficulty achieving high levels of accuracy and precision, limited materials, and time-consuming maintenance requirements. Despite these drawbacks, 3D FDM printing has a wide range of potential applications and will likely continue to be an important tool in manufacturing for years to come.