If you are passionate about 3D printing or transforming digital creations into physical items, you might consider launching your own 3D printing company. Producing a product in this industry allows you to put your creative and technical abilities to work.
Knowing more about 3D printing and the various business opportunities it presents might assist you in deciding whether or not this is the best route for you to take. In this post, we will discuss what 3D printing is, how to establish a business specializing in 3D printing, and why you would want to start such a firm.
What Do You Need to Start 3D Printing?
In recent years, 3D printing has become a hobby and a line of work. Countless options are available, from making prototypes to creating unique parts and figurines. But what are the prerequisites for 3D printing? These are the key points:
1. 3D Printer:
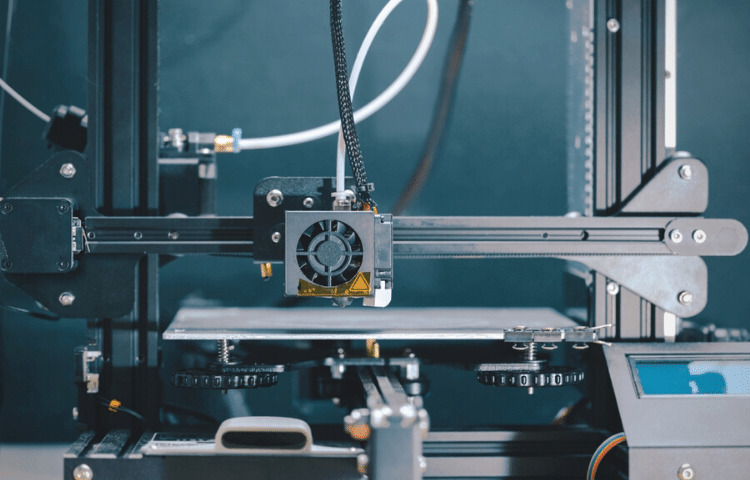
A 3D printer is the first thing you need to start 3D printing. There are many different types of printers on the market, each with its benefits and drawbacks. Stereolithography (SLA) printers provide high-resolution prints, while Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) printers are well-liked for their accessibility and affordability. SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) printers are pricey and frequently used in the industry.
Consider print quality, build volume, and price when selecting a 3D printer. Checking the printer’s compatibility with the materials you intend to use is also crucial.
2. Filament:
The substance used to make 3D prints is filament. Many different kinds of filament exist, including PLA, ABS, PETG, Nylon, TPU, and others. Because of its low cost, low warping, and simplicity of use, PLA is a great material for beginners. PETG is extremely resistant to impacts and weather conditions, but ABS is renowned for its strength and durability.
It’s critical to choose the appropriate filament for your 3D printing project. Consider the material’s characteristics, such as its durability, flexibility, temperature resistance, and strength.
3. Computer and 3D Modeling Software:

To develop and produce 3D models, a computer and 3D modeling software are needed. Software for 3D modeling comes in both free and commercial versions, with differing degrees of sophistication. Beginners often turn to free tools like Tinkercad and Blender, while pros frequently utilize more sophisticated programs like Fusion 360 and SolidWorks.
The 3D modeling program you use will rely on your degree of expertise, your budget, and the project at hand. Making ensuring the software is compatible with your 3D printer is crucial.
4. Accessories:
A print bed, calibration equipment, and slicing software are just a few of the extras needed to guarantee a seamless 3D printing experience. The surface on which a 3D object is printed is called a print bed. Calculator equipment like a caliper or feeler gauge is required to calibrate the printer bed and guarantee optimal print adhesion.
The 3D model is prepared for printing using slicing software, such as Cura or Simplify3D, by breaking it unto layers and producing G-code. Applying the correct slicing parameters is essential to get the required print quality.
How Much Does it Cost to Start a 3D Printing Business?
Many variables, including the size of the business, the kind of 3D printing technology utilized, the materials and equipment needed, and the firm’s location, can significantly impact the cost of launching a 3D printing company. To give you a basic sense, though, here are some estimates:
Cost of the equipment: The price of a 3D printer can vary greatly, from a few hundred dollars for entry-level consumer printers to tens of thousands of dollars for top-of-the-line industrial printers. You might start with a basic consumer-grade printer to keep expenses down as a company.
Costs of Materials: Depending on the type of 3D printer you use and the materials you choose to print with, the cost of materials can also vary significantly. While more sophisticated materials like Nylon or ABS may cost up to $100 or more per kilogram, basic PLA filament can cost between $20 and $30 per kilogram.
Overhead Costs: Rent, utilities, insurance, and marketing charges are a few examples of overhead costs to consider. These prices might vary greatly depending on the business’s location and size.
It may cost $5,000 to $15,000 to launch a small 3D printing firm, but larger enterprises would need expenditures of $50,000 or more. To correctly project the startup expenses for your 3D printing firm, conduct your homework and draft a thorough business strategy.
How to Start a 3D Printer Business?

Consider adhering to the following procedures to get your 3D printing company off the ground:
1. Get knowledgeable about 3D technologies:
Learning about recent 3D printing applications and technologies will help you produce high-quality items and make wise business decisions. Understanding how to use 3D printers and perform rapid repairs is crucial, so that tiny production bottlenecks don’t ruin your day.
Finding institutions that offer degrees in 3D printing might be difficult. Still, many offer online courses and certificates in using the machines and producing the digital models they replicate.
2. Choose a Market:
Decide what your company will manufacture after you are familiar with the principles underlying the operation and creation of 3D-printed objects. It’s useful to consider local demand, such as whether a rising entrepreneurial scene needs prototypes or a local tabletop game community would want tiny figurines.
Appealing to current markets might assist your firm in gaining clients. To target an established market, consider contacting organizations and groups you may partner with to learn more and broaden your influence.
3. Create a Plan of Action:
Choose if you will work from home and whether you will have one other employee. If you want to launch a home-based business, think about where you can set up shop and how many printers you can effectively run in that area.
Finding more impartial or online settings to meet potential customers or investors may also be necessary. It’s advantageous to consider leasing your printers and exporting them to other firms for extra money as your product grows if you want to make a unique item.
4. Choose a 3D Printer:
Consider this while deciding which 3D printer is best for you: you might not require a large-scale, industrial machine. It’s crucial to keep inside your means and choose printers compatible with your supplies. One powerful 3D printer, for instance, might produce little, intricate parts. But, numerous mid-range 3D printers would be more suited if you plan to make larger, simpler items, such as kitchenware.
Also, searching for 3D printers that provide extras like a warranty or customer service might be beneficial. They may assist with problems as you work and guarantee that production moves smoothly.
5. Research Filaments:
The various materials for 3D printers are called filaments. It would be best to study which filament is ideal for your product because use and the circumstances needed to print without warping might differ. Here is a list of a few popular filaments, along with each one’s benefits and drawbacks, to help you get started on your study and get an idea of what would work for your product:
ABS: Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene is tough and affordable, but it also emits obnoxious fumes and necessitates a heated printing bed.
Sandstone: Although it doesn’t need a printer bed and has a distinctive outer appearance, this material isn’t as durable as others.
Wood: Compared to other materials, wood is more pliable after printing and has customizable aesthetics and hues.
Metal: Metal is strong and doesn’t require a hotbed, although shaping it could take longer.
Flexible TBE: This substance has a rubbery elasticity and excellent form but requires a little tweaking to come out of the nozzle.
6. Select a Platform and Brand:
The last step is to pick a name and brand for your new company before promoting yourself and selling your goods. You must set your company apart from the competition and successfully convey its services.
You might design a website and other social media sites with a logo or label. Use the logo as a starting point for the decor and store design if you start with a real location. Moreover, several platforms let designers run stores directly from their websites.
Why Should One Begin Their Own 3D Printing Business?
Sustainability:
Most of the processes used in 3D printing generate very little to no waste, and the additive layering process utilizes all or the vast majority of the material. 3D printing utilizes many filaments, many of which are recyclable or degradable. As a result of the short amount of time required for production, 3D printing may also require less energy than traditional industrial production lines.
Efficiency:
Because 3D printing is already efficient compared to industrial production, so meeting the rising demand for goods is less of a logistical headache for manufacturers. It also means that customers do not have to worry about ordering an insufficient amount to justify production or an excessive quantity that will overload production.
Neither of these scenarios is a concern. Because 3D printers optimize multi-step processes, your business can continue functioning efficiently even if you offer additional services, such as cleaning and sanding, for your products.
Profitability:
Even if you sell a product that caters to a specific market, you can prevent excess inventory by basing your company’s production and sales model on the principle of “on demand.” You are only required to invest resources into producing goods when a customer orders one of your offerings; consequently, there is no risk of the company losing money.
You may be able to start a business with more financial restraint if you take a no-excess approach by following these guidelines. If you are running your 3D printing business as a side job, this may also be helpful.
Flexibility:
The degree of automation in the three-dimensional printing process is directly proportional to the scope of the goods and services the printer intends to produce.
This may enable you to advertise yourself and the company more, or you may spend additional time expanding your knowledge and abilities regarding the construction of models and other filament-related operations. Moreover, it gives you the ability to schedule when your production will take place.
3D Printing Industry Trends:
The industry for producing 3D printers in the United States has robustly recovered from the pandemic recession. There is a window of opportunity for enterprising individuals willing to take risks to ride the wave.
The Size of the Market and Its Expansion:
- The market size of the 3D printer manufacturing sector in the United States has returned to a high growth path, hitting revenue of $6.3 billion, the highest it has been in the previous ten years. This growth rate is the greatest it has ever been. Since 2017, the market has had an average annual growth of 14%me.
- The global market for 3D printing, currently valued at $14 billion, is anticipated to expand at a rate of 30% annually and reach $63 billion by 2026.
- The United States is home to 131 companies producing 3D printers.
- The industry is responsible for the employment of 5,000 persons in total.
The following are some current trends in 3D printing:
- The development of new technologies is paving the way for the creation of numerous new applications for 3D printing, which is propelling the expansion of the sector. The production of prototypes continues to be the most prevalent application for a 3D printer; nevertheless, additional applications include the creation of toys and home decor.
- The development of new materials that can be printed using 3D printers, such as polymers and metals, is contributing to the sector’s progress. Components for new tools and even fully assembled vehicle parts are examples of new items that may be manufactured using 3D printing.
There are other challenges to be found in the 3D printing sector, which include the following:
- The possibility for printers to replicate patented items poses a risk to intellectual property rights brought about by the rise of 3D printing. This may result in more stringent regulations for 3D printing.
- Because rapidly developing technologies have the potential to render existing 3D printers outdated, organizations that specialize in printing will need to upgrade their machinery routinely.
How Much Money Is It Possible to Make With a 3D Printing Business?
The cost of 3D printing can range from thirty to one thousand dollars or more, depending on the level of detail required. The designs are likely to be complicated if you specialize in prototypes; thus, for the sake of these calculations, we will estimate that the average cost is $500. After deducting the cost of the ingredients, you should have a profit margin of about 80 percent.
You could be able to start working from home within the first year or two of your business and pull in $130,000 annually by selling five prints each week. Assuming a margin of 80 percent would result in a profit of more than 100 thousand dollars.
As more people get familiar with your brand, you may find that weekly sales increase to 25 prints. At this point, you would have to rent a commercial location and pay workers, bringing your margin down to thirty percent. With anticipated yearly sales of $650.000, your profit would be close to $200,000 yearly.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Is A 3d Printing Business Profitable?
Certainly, a 3D printing company may be successful. The business’s potential to remain profitable will be influenced by several variables, including the price of supplies and machinery, the level of market rivalry, the demand for 3D printing services, and the capacity to produce superior and distinctive goods. A 3D printing firm may boost its chances of success and profitability by conducting thorough market research, creating a sound business plan, and using effective marketing techniques.
How To Start A 3d Printing Business From Home?
- Find your target market by conducting market research.
- Choose the 3D printer type and resources you’ll need to satisfy your clients’ demands.
- Your beginning expenditures, pricing strategy, and marketing approach should all be included in your company plan.
- Create a workplace in your house with enough lighting, ventilation, and storage.
- Buy or rent the required tools and supplies.
- Get any licenses or permissions that are required for your business.
- Create a website or a presence on social media to promote your goods and services.
- Use networking, advertising, and referrals to market your company.
- To earn a good reputation, offer top-notch goods and first-rate customer support.
- To be successful and competitive, you must constantly review and modify your business plan.
How To Start A 3d Printing Farm?
Several 3D printers are used in a 3D printing farm to manage higher output volumes. To launch one, you must perform market research, create a business strategy, decide on a site, buy or rent supplies and equipment, employ people, implement quality control procedures, and advertise your offerings.
Bottom Line:
It may be rewarding and successful to launch a 3D printing company. It’s crucial to conduct careful market research, create a compelling business strategy, and invest in tools and supplies, whether you intend to run your business from home or manage a 3D printing farm. You may create a prosperous 3D printing firm by offering top-notch goods and first-rate customer service and regularly assessing and revising your business plan. There are endless opportunities to create and develop in this fascinating business as 3D printing technology continues evolving and flourishing.




